Processing of titaniferous magnetite ore in MAGMA
The Urals region (Russia) experiences an acute deficit of iron ore for blast furnaces of metallurgical plants. Iron ore has to be brought in from remote regions (Karelia, central Russia, East Siberia, etc.). At the same time, Chelyabinsk province (Urals, Russia) has large deposits of titano-magnetite ore with high contents of TiO2 and Vn.
Complex processing of such ores by blast furnaces is practically impossible because of formation of high-melting-point slag with a high TiO2 content.
The task of efficient and complex processing of titano-magnetite ores is solved by using highly efficient cooling system of the smelting unit MAGMA that allows to use high temperatures in the working space of the smelting chamber (Figure below).
The result of primary separation of titano-magnetite ores is vanadium cast iron and titaniam slag, from which the following products can be produced at later stages of complex processing: vanadium slag (raw material for the production of vanadium alloys), steel, ferro-titanium, high titaniam slag (raw material for a TiO2-based coloring pigment, titanium sponge).
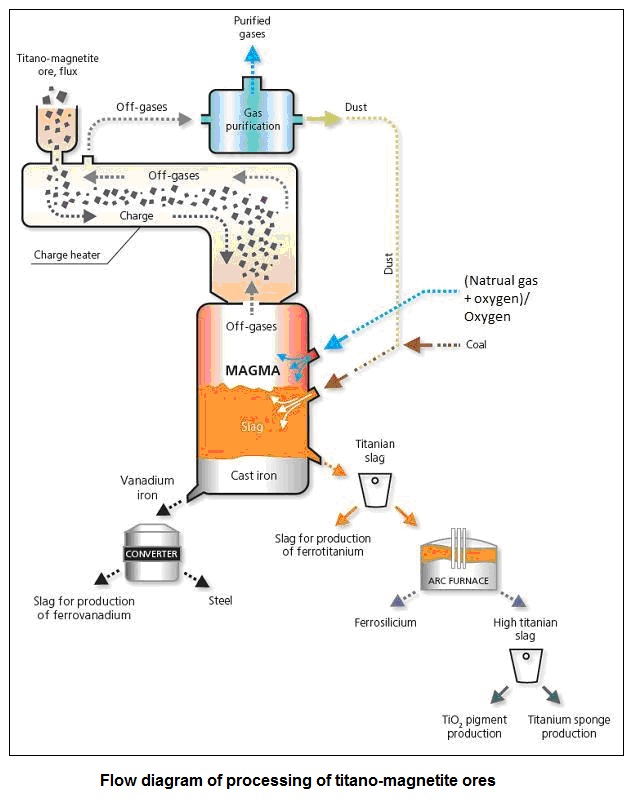
Processing of titano-magnetite ore by the proposed technology is completely waste-free.
